, OH
This 48-acre farm is the last remnant of an agricultural way of life that characterized Parma Township well into the 20th century. The farmhouse, built circa 1855 by Western Reserve settler Lyman Stearns, is representative of the Greek Revival style of architecture popular in this region prior to the Civil War. The “Yankee” style barn predates the house. Suburban development following World War II engulfed virtually all of this area by the 1950s. The Stearns Homestead was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1981. (continued on other side)
, OH
American Legion Union Post No. 79 was organized on August 21, 1919, at the National Guard Armory in Marysville. In 1927, the Legion purchased a 24 acre parcel known as “Clement Woods” to serve as a living memorial “to Union County Veterans of All Wars”. The park was dedicated on August 24, 1927, and renamed American Legion Memorial Park. The brick Memorial Building was constructed from 1937 to 1938 by the Works Progress Administration (WPA). The Post held their first meeting there on September 12, 1938. An addition to the Memorial Building was completed in 1960. In 1989, the Legion donated the park to the City of Marysville on the condition it remains a free, public park.
, OH
In 1820, Mark Evans, John Davis, and Jacob Waggoner acquired from Daniel Triplett an 18-rod-square parcel (approximately two acres) at this location on which to build the first school in Plain Township. Education was not publicly funded at the time and the first teacher, Jacob Smith, “kept” school for $1.50 per scholar. The fact that part of the school lot became a cemetery suggests that the log building was also used for church services, as was a log school a mile and a half east of here on Central College Road. (continued on other side)
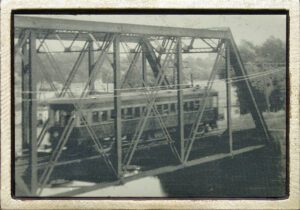
, OH
At this site the Lake Shore Electric Railway crossed a bridge that spanned the Vermilion River. The western abutment of the former bridge is plainly visible just below along the river bank. Widely known as the “Greatest Electric Railway in the United States,” the flaming orange trolley cars of the Lake Shore Electric Railway transported people and freight for thirty-seven years (1901-1938) along the southern Lake Erie shores from Cleveland to Toledo often reaching speeds of sixty miles per hour. The interurban line played a primary role in the development of the western Cleveland suburbs and also carried throngs of summer visitors to Lake Erie recreation facilities at Avon Beach Park, Linwood Park, Crystal Beach, Mitiwanga, Ruggles Grove, Rye Beach, and Cedar Point. The power lines still standing along the system’s right-of-way attest to the fact that it also assisted in bringing electric power to the entire region.
, OH
The Cincinnati Museum of Natural History is part of Cincinnati Museum Center. The Western Museum Society, organized by Dr. Daniel Drake in 1818, preceded it. The Western Museum Society’s collection was built around ornithology, fossil zoology, geology, and Native American artifacts. The Museum’s first taxidermist, John James Audubon was hired in the winter of 1819 to do taxidermy, build collections, and create exhibits. Audubon supplemented his income by drawing portraits, teaching art, and running his own drawing academy. During his brief stay in Cincinnati, Audubon created five paintings of local birds that were among the first contributions to his acclaimed Birds of North America. He left Cincinnati in 1820 to travel and finish his collection of drawings that would make him one of North America’s most revered and famous nineteenth century artists.
, OH
The Indian Point Site contains the remains of a prehistoric Native American earthen enclosure, officially known as the Lyman site, named after a former property owner. The site contains two earthen walls that are bordered by ditches. Steep cliffs provide natural barriers on two sides of the enclosure. Archaeological digs have uncovered many artifacts here, including pottery sherds, tools, pipes, and beads. There is evidence that the walls were built around 140 B.C., and the site was occupied again around 1500 A.D. by the Whittlesey Tradition people. It is uncertain if the site was a village or was used as a ceremonial center. After 1650 A.D., the area became a neutral hunting ground for various historic tribes.
, OH
During the American Revolution, Fort Laurens became the only Continental military fort in what would later be Ohio. Continental army troops and militia, led by General Lachlan McIntosh, built the fort between November-December 1778. Named for the president of the Continental Congress, Henry Laurens, the army intended to use the fort to launch an offensive against British-held Fort Detroit, observe enemy movements, and stage attacks on British-allied Indian villages. To fulfill terms in the “Treaty with the Delaware” (1778), McIntosh chose a site about two miles south of the “Great Crossing” on the Tuscarawas River in friendly Lenape (Delaware) territory. (Continued on other side)
, OH
For more than two centuries, this burial ground has been a final resting place for those individuals whose lives represented the community history of Canfield. The earliest existing tombstone marks the death of Huldah Tanner in 1803. Seven earlier deaths in Canfield Township are recorded from 1798 to 1803, but the gravesites are unknown. Elijah and Rhoda Hopkins Wadsworth formally deeded the cemetery to the citizens of Canfield in 1810 with a first edition of land donated by Matthew B. Whittlesey in 1811. In 1862-1863, the graveyard was again enlarged. For seventy years the cemetery and fencing were maintained on a volunteer basis. When the Village of Canfield was incorporated in 1869, the care and management was vested in a board of trustees. (continued on other side)