, OH
This section of the Miami and Erie Canal, constructed from 1833-1837, was vital to this region’s commerce and development. It allowed for farmers and businesses to get their goods to larger markets at a lower cost and faster speed than by hauling overland. Passengers could also travel across the area by canal boat. John Clark saw the location of the Lock 15, situated in Monroe Township at the junction of the Milton-Carlisle Pike (Main Street), as an opportunity and in 1840, platted the new town of Tippecanoe City (now Tipp City). Many types of commerce and trade grew up around the canal including boarding houses, saloons, a tannery, and a mill. Some of the original buildings still stand, such as a mill to the west of Lock 15, John Clark’s home at the southeast corner of Main and First streets, and the hotel at the northeast corner of Main and Second streets.
, OH
Harry Coulby was born of humble farming parents on January 1, 1865 in Claypole, England. At age 17, he immigrated to Cleveland to realize his dream of sailing the Great Lakes. He did not become a sailor, but instead became the commanding figure in the ore shipping trade. In 1886, Pickands Mather Company employed him, and Coulby, with imagination and a willingness to work, made the movement of ships and cargo his career. Within 20 years, he managed 100 ships, controlling the two leading fleets. He was described as the “Czar of the Lakes,” a tribute to his leadership qualities. Adopting President Abraham Lincoln’s method of making a point with a story, he became Wickliffe Village’s first mayor in 1916. His home, known as Couallenby, became the city hall. Harry died while visiting his birthplace on January 18, 1929, and was laid to rest in the churchyard that he had restored.
, OH
Civic organizations played pivotal roles in the development of the residential community of Hazelwood, founded as a subdivision of Blue Ash in 1888. The Hazelwood Civic Association, initially established as the Brothers Civic Society in 1941, addressed community needs by working for public improvements and promoting civic relations through social events and educational programs. Efforts by the HCA led to the construction of a new civic center and the introduction of the Boy and Girl Scouts and other programs that were previously unavailable to African-American children. Hazelwood’s deterioration and the threat of encroaching industrial development led to the formation of the Hazelwood Improvement Corporation in 1968. The HIC, acting as an agent of the city of Blue Ash, helped to upgrade housing, pave roads, build new homes to ensure a residential nature, install water and sewage systems, and erect streetlights. In 1997, the Hazelwood Community Association was organized to assist residents during Hazelwood’s transition to a racially integrated community.
, OH
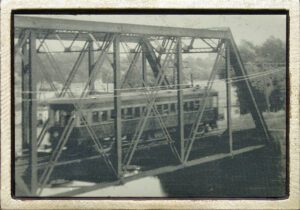
At this site the Lake Shore Electric Railway crossed a bridge that spanned the Vermilion River. The western abutment of the former bridge is plainly visible just below along the river bank. Widely known as the “Greatest Electric Railway in the United States,” the flaming orange trolley cars of the Lake Shore Electric Railway transported people and freight for thirty-seven years (1901-1938) along the southern Lake Erie shores from Cleveland to Toledo often reaching speeds of sixty miles per hour. The interurban line played a primary role in the development of the western Cleveland suburbs and also carried throngs of summer visitors to Lake Erie recreation facilities at Avon Beach Park, Linwood Park, Crystal Beach, Mitiwanga, Ruggles Grove, Rye Beach, and Cedar Point. The power lines still standing along the system’s right-of-way attest to the fact that it also assisted in bringing electric power to the entire region.
, OH
After the outbreak of the Civil War in the spring of 1861, the U.S. War Department commissioned Ohio Senator B.F. Wade of Jefferson and local Congressman John Hutchins of Warren to supervise the Union Army’s recruiting service in Northeastern Ohio. Recruitment rolls were to be filled in summer so training could be conducted during the fall. The Oak Grove Fairgrounds in Warren, home of the Trumbull County Agricultural Society, was one of the sites selected for the training. This camp was named Camp Hutchins in Congressman Hutchins’ honor. John Hutchins, an attorney by profession, had served as Trumbull County Clerk of Courts and had been assocaited with future Ohio governors David Tod (1862-1864) and Jacob Cox (1866-1868), in their law firms. An ardent anti-slavery man and Underground Railroad agent, Hutchins served in the U.S. Congress from 1859 to 1863.
, OH
The American Sheet and Tin Plate Company founded the first Dover Public Library for the benefit of its employees at the corner of Front Street and Factory Street in 1902. Five years later, the library moved to a residence on Cherry and Fifth Streets. In 1916 the city dismantled “the old Downey residence” and built a high school in its place, with the public library occupying the basement. In 1934, the library moved to a converted residence at 417 North Walnut Street. Over time, however, the building became inadequate to house this beloved institution. In 1953 the city of Dover passed a bond issue to build a new library for the community. The new building, located at this site, opened in 1955.
, OH
This single lane Pleasant Valley Road Bridge was constructed in 1881 by the Wrought Iron Bridge Company of Canton, Ohio, and is a 163 foot-long Whipple Truss (double intersection Pratt through truss). It replaced a wooden bridge that portaged the west branch of the Chagrin River a few hundred yards downstream. The structure, one of less than ten of its kind remaining in the state of Ohio, and possibly the longest in Lake County, was built to sustain the Euclid-Chardon Road traffic on U.S. Route 6. Known as the Grand Army of the Republic Highway, G.A.R., this major thoroughfare served this purpose until 1952 when a new high level bridge bypass was constructed to the south. The Truss bridge, pleasing to the eye with the artwork and name plates atop the overhead portals, was designed to enhance the bridge’s appearance within the valley. (Continued on other side)
, OH
The Cincinnati Union Terminal opened in March 1933 and integrated rail travel in the city, which previously operated from five separate passenger terminals. Built when rail travel was already in decline, Union Terminal stopped operating as a passenger railroad station in 1972. Only during WWII was the terminal used to capacity with as many as 34,000 people travelling through the building daily in 1944. As part of preservation efforts, 14 mosaics depicting Cincinnati industry of the 1930s by Winold Reiss were saved from the concourse and moved to the Greater Cincinnati Airport. The restored Union Terminal became a Museum Center in November 1990 with the opening of the renovated Cincinnati Museum of Natural History and new Cincinnati History Museum. Cincinnati Union Terminal has been described as one of the most outstanding examples of Art Deco train stations in the nation and was listed on National Register of Historic Places in 1972.