, OH
The Ohio and Erie Canal was Ohio’s solution to the lack of a reliable and fast transportation system to move goods to outside markets. The canal opened in the then unplatted village of Groveport on September 25, 1831 and contributed directly to Groveport’s success as a center of commerce. W.H. Richardson built lock 22, the only lock in Groveport, as part of his bid to build section 52 of the canal. Lock 22, the last lock before a series of locks in Lockbourne, Ohio that lower the canal to the level of Big Walnut Creek, is 90 feet long with a 15 foot wide lock channel. A variety of businesses clustered along the banks of the canal. In the mid-nineteenth century, a canal boatyard and dry dock was operated in what is now Blacklick Park. Canal boats were built and repaired in this facility that was considered the first notable such operation on the canal below Baltimore, Ohio.
, OH
Born in Rhode Island, John Pray (1783-1872) moved to the Maumee River Valley from New York shortly after serving in the War of 1812 and completing a prospecting tour in Ohio. He built a dam across the river to Granger Island and in 1821 constructed a water-powered gristmill, the first on the lower Maumee. In 1831, he laid out the Village of Waterville with the first 50 lots. The Columbian House, a stagecoach inn constructed by Pray in 1828 and expanded in 1837, was for years the commercial and social center of Waterville and accommodated travelers from cities such as Detroit and Cincinnati. From this building, he operated the village’s post office. When Wood County was organized in 1820, Pray became a commissioner until Lucas County was formed from part of Wood in 1835. For nine years he served as Justice of the Peace in Waterville. He and his wife Lucy raised eleven children to adulthood. Circa 1854 he constructed his home, which today overlooks Pray Park.
, OH
Thousands of Irish immigrants came to Columbus to seek personal and religious freedom. With the “Great Hunger” in Ireland and the completion of the Ohio and Erie Canal and the National Road, immigration to Columbus increased in the mid nineteenth century. They initially settled in the north side of the city in the swamp flats, where inexpensive land was available and work could be had on the railroads. Settlement spread to Franklinton, on Naghten Street, later known as “Irish Broadway”- part of which is now Nationwide Boulevard, and to nearby Flytown. The immigrants became domestic workers, civil servants, entrepreneurs, and served the city in police and fire departments. Others were leaders in government, law, medicine, and education. Their legacy continues today in the Irish-American population of Columbus, Ohio.
, OH
Sylvania was once the headquarters for the Toledo and Western Railway, an electric interurban line that provided service between Toledo and Pioneer with a branch line to Adrian, Michigan. Construction began here in 1900 with planning and specifications set to steam railroad standards. With completion of rails, a powerhouse, maintenance facilities, and offices, the Toledo and Western Railway Company was soon in the business of providing freight and passenger service and was especially competitive as it owned more freight engines than most interurban lines. Operating an electric interurban line also meant that the company had the ability to provide electricity to people living in Sylvania and to other communities and property owners living along the line’s right-of-way. Besides freight, passengers, and electricity, Toledo and Western also provided postal service, one of the first interurban lines to do so. [continued on other side]
, OH
John Malvin (1795-1880) was an operative on the Underground Railroad and an ardent member of anti-slavery and abolitionist causes. Born in Dumfries, Virginia of a free mother and enslaved father, Malvin was apprenticed at an early age to learn carpentry and taught himself to read and write. In 1827, he moved to Cincinnati where he became an ordained preacher and an activist in the cause of freedom. In 1831, with his wife Harriet, he moved to Cleveland where he became a charter member of the First Baptist Church, a sawmill operator, and captain and owner of the canal boat Auburn. (continued on other side)
, OH
Three hundred yards east of this location on Oak Road, overlooking the Miami & Erie Canal, was the house of abolitionist John Van Zandt (1791-1847). For years this house was known as one of the most active “stations” on the Underground Railroad. In 1842, two bounty hunters from Sharonville caught Van Zandt helping eight runaway slaves who had escaped from owner Wharton Jones of Kentucky. Defended in court by Salmon P. Chase, who became Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1864-1873, Van Zandt was convicted and fined. Chase appealed the case to the U.S. Supreme Court, where he tested the constitutionality of the 1793 Fugitive Slave Law. When writing her novel Uncle Tom’s Cabin, Harriet Beecher Stowe used Van Zandt as the abolitionist character John Van Trompe. Van Zandt’s house became associated with the book and was known as “The Eliza House,” named for one of the novel’s main characters.
, OH
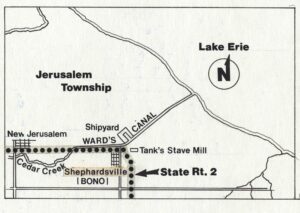
To utilize the area’s rich timber stands, Detroit industrialist Eber Brock Ward (1811-1875) built a canal around 1870 in what was then Oregon Township, Lucas County. Known as Ward’s Canal, it stretched approximately 2-3/4 miles through wetlands to Lake Erie. Through the canal passed timber sawn at Ward’s mills and ships from his boatyards. Two settlements formed to house workers: Shepherdsville, renamed Bono in 1898, and New Jerusalem. (Continued on other side)
, OH
The Cozad-Bates House is one of the oldest remaining structures in Cleveland’s University Circle. The original section, built circa 1853, is the only pre-Civil War residential structure left in the neighborhood. Built by Samuel and Jane Cozad’s son, Andrew Cozad, the first section used locally made brick to form a simple two-story, one-room-deep, vernacular English-I house. The family owned a large portion of the land which is now occupied by University Circle. Justus Cozad, Andrew’s son, returning from the west where he worked as a railroad superintendent and civil engineer, built the later section on Mayfield Road for his larger family in 1872. It is a rare surviving example of Italianate-influenced residential architecture, including a hipped roof, curved bay windows, paired eave brackets, and prominent belvedere. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974 and designated as a Cleveland Landmark in 2006.