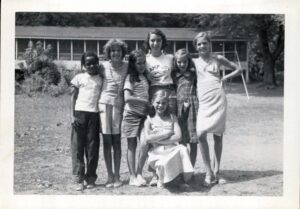, OH
On October 4, 1957 the Soviet Union surprised the world with the launching of Sputnik 1, the world’s first artificial satellite. The Cincinnati Astronomical Society’s Moonwatch Team, organized in 1956 as part of its participation in the International Geophysical Year, was immediately activated by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (S.A.O.). First observations of satellites were made December 15, 1957. On these grounds, from 1957 to 1964, the Cincinnati Moonwatch Team, principally under the leadership of Tom Van Flandern (1940-2009), spent thousands of man-hours optically observing and recording data to verify the positions of satellites in space. Many times the team compiled the best satellite tracking records in the world. Because of this work The Moonwatch Team and the Cincinnati Astronomical Society were recognized by the S.A.O. as one of its leading teams worldwide.
, OH
John T. Crawford (1813-1880), was a white Union soldier. In gratitude for the kindnesses he received from African-Americans during the Civil War, Crawford willed his 18 1/2-acre farm to be used as a “home, for aged, indigent worthy colored men, preference to be given to those who have suffered the miseries of American Slavery.” The Crawford Old Men’s Home opened in 1888 and operated until 1964 under the trusteeship of prominent African-Americans such as lawyer William Parham, newspaper editor Wendell Dabney, and Ambassador Jesse D. Locker. It merged with the Progressive Benefit Society’s Home for Colored Women to become the Lincoln Crawford Nursing and Rehabilitation Center. Pleasant Hill Academy, College Hill Library, and Crawford Commons are all on the site of the Crawford farm.
, OH
Camp Joy was born at the site of Seven Hills Neighborhood House and original location of St. Barnabas Episcopal Mission Church. Displacement and loss caused by Ohio River flood of 1937 inspired St. Barnabas’ rector and his wife, Laurence “Cap” and Sadie Hall, to act on behalf of the children of Cincinnati’s West End. The Halls conceived of Camp Joy as a haven where kids could find a respite from impoverished surroundings in the city and its sweltering summer heat. The camp was a success and continued after the Halls’ assignment to another parish. From 1940-1944, Rev J. Brooke and Mrs. Betty Mosley continued to nurture the people of the West End through St. Barnabas and Camp Joy. (Continued on other side)
, OH
Fr. John Henni founded St. Aloysius Orphanage in 1837 to care for German-speaking Catholic children who were left abandoned by the cholera epidemics of the 1830s. The orphanage has occupied its main building since 1856. All of the orphanage’s other buildings were constructed by 1930. In 1864, additional land was purchased, making the orphanage a self-sufficient farm growing fruits and vegetables as well as livestock.
, OH
Confederate Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan’s Indiana-Ohio Raid, or Great Raid, from July 2-26, 1863 covered nearly 1,000 miles and penetrated deeper into the North than any other Confederate incursion during the Civil War. The raid was also the only significant military action of the war in Ohio. Union cavalry chased Morgan’s 2,000 cavalrymen across twenty-four Ohio counties after the troopers entered the state from Indiana. On July 13, 1863 Morgan’s main column encountered no resistance as it passed through New Haven, about five miles north from this site. (Continued on other side)
, OH
Reverend Richard E. Scully, founder of the Cincinnati Goodwill operated a Fresh Air Camp for women and children in the 1930s and 40s. The camp was part of a 100-acre site with vegetable fields, a swimming pool, tennis courts and horseshoe pits. The farm house on site was used as lodging for visitors. Men who worked at the camp received food and other forms of relief for their families. Vegetables produced on site were distributed at the Goodwill location at Ninth Street and Freeman Avenue in Cicinnati. According to family stories, Ruth Ann Eldridge, the frist child of Edison and Anna Eldridge, was buried on the site of the camp in 1933. Rev. Scully had officiated at Edison and Anna’s wedding and was a friend of the family.
, OH
In 1910, voters approved a $275,000 bond issue to construct this school on seven and one-half acres of an old orchard on Sherman Avenue. Opened in 1914, Norwood High School offered standard educational classes as well as home economics, manual training, and commercial courses. Increased enrollment required additions of an east wing in 1924, a west wing in 1931, and a field house in 1927. Adding a technical building in 1950 provided Norwood with one of the first vocational education programs in the area. A source of community pride, this building has been a high school, junior high school, and middle school.
, OH
James Norris Gamble, entrepreneur, industrialist, philanthropist and civic leader, is best known for inventing Procter & Gamble’s Ivory Soap, the “soap that floats,” in 1878. Applying a scientific approach, Gamble transformed P&G into a nationally recognized corporate leader and creator of consumer products for a rapidly growing America. Beyond P&G, Gamble financed early efforts to educate freed southern slaves as an original sponsor of the Freedmen’s Aid Society. Later, he underwrote civil rights leader Mary McLeod Bethune’s work to educate poor African American women. In Cincinnati, Gamble’s philanthropy included endowment of Christ Hospital and the founding of its Institute of Medical Research. Gamble funded completion of University of Cincinnati’s Nippert Stadium in 1924 as a tribute to his late grandson.