, OH
The Temple of Rumley Church is of one of two remaining buildings in what once was Rumley, a thriving African American community in Shelby County. On May 19, 1837, the village was surveyed for Amos Evans, who built his hewed log dwelling and store. Brothers Joel and George Goings (aka. Goens), freed black men from Monongalia County, Virginia, purchased 80 acres of land that same year. They settled with their families near Rumley in Van Buren Township along with other free men and women of color, including former slaves. Joel Goings erected the first brick house in 1841, using bricks from his own brickyard. By 1846, the Rumley community stretched over 7,000 acres and included the Collins, Redman, Williams, Davis, Lett, and Brown families. (Continued on other side)
, OH
This cemetery stands as evidence of a once thriving African American farming community established in the 1820s. With the aid of community leader, Alexander “Sandy” Harper (c.1804-1889), Captina, originally called Guinea, became a stop on the Underground Railroad, a national network, shrouded in secrecy, of volunteers who directed slaves northward. Harper is buried in this cemetery, along with Benjamin Oliver McMichael (1865-1941), an educator who taught for twelve years in Captina/ Flatrock at a segregated schoolhouse. There are 113 known burials in the cemetery, including nine Civil War veterans. At this site in 1825, an African Methodist Episcopal Church was established to serve the community. Many of its members left Captina to work in cities, but the church continued services until 1962. The building then fell into disrepair and collapsed during a windstorm in 1978.
, OH
Established in 1879 by Chicago industrialist William P. Rend as a coal mining town, Rendville became a place where African Americans broke the color barrier. In 1888, Dr. Isaiah Tuppins, the first African American to receive a medical degree in Ohio, was elected Rendville’s mayor, also making him the first African American to be elected a mayor in Ohio. Richard L. Davis arrived in Rendville in 1882 and became active in the Knights of Labor. He was one of the labor organizers from the Little Cities of Black Diamonds region who helped found the United Mine Workers of America in 1890. An outstanding writer and orator, Davis was elected to UMWA’s national executive board and organized thousands of African Americans and immigrants to join the union. (continued on other side)
, OH
Raised in an Ohio orphanage, Warren G. Grimes (1898-1975) ran away after finishing the ninth grade and at age 16 went to work for the Ford Motor Company in Detroit. He later became a partner in an electrical business where he was instrumental in designing and developing the first lights for the Ford Tri-Motor airplane. In 1930 Grimes moved to Urbana and founded a small lighting fixture plant, Grimes Manufacturing. The inventor of the familiar red, green, and white navigation lights found on the wing tips and tails of aircraft, Grimes, known as the “Father of the Aircraft Lighting Industry,” also developed other aircraft fixtures, including landing, instrumental, and interior lights. Every American-made airplane flown during World War II was equipped with Grimes lights. Grimes served as mayor of Urbana and chairman of the State of Ohio Aviation Board.
, OH
The Ohio River, the southeast border of Gallia County, played a significant role in the development of Gallipolis and Gallia County. One of the state’s first thoroughfares, this waterway enabled pioneers to settle in what was known as the Northwest Territory. On October 17, 1790, approximately 500 French immigrants arrived in Gallipolis, traveling by flatboats from Pittsburgh, and settled in log cabins in what is now City Park, in the heart of Gallipolis. This established the second oldest permanent settlement in the territory. The settlers relied on the River for communication, commerce, and transportation, and the River brought postal service to Gallipolis in 1794. As local business and river trade developed in the 1800s, Gallipolis became a thriving port. The scenic Ohio River is an important inland waterway, providing transportation for many commodities between major cities. The River also provides recreational opportunities for both visitors and residents, including water sports, fishing, and boating.
, OH
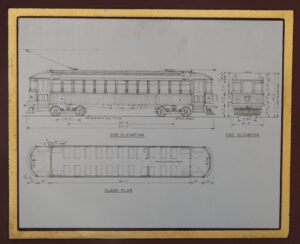
The Dayton, Springfield, and Urbana Electric Railway (DS&U) was an “Interurban” rail system that ran between the cities of Urbana, Springfield and Dayton. Its beginning can be traced to the franchise given to William H. Hanford to operate a single line of electrical railway between Springfield and the southern boundary of Champaign County in 1895. Hanford then sold his rights to John G. Webb of Springfield and Colonel Frederich Colburn of Kentucky, who along with other syndicate members formed the Dayton, Springfield, and Urbana Electric Railway. In 1897 Boston promoter Arthur E. Appleyard joined the syndicate and brought investment monies, organizational skills, and energy to the venture. He quickly became managing director/treasurer and the real driving force of the DS&U. The railway was organized into two divisions. One operated between Dayton and Springfield and the other between Springfield and Urbana. [continued on other side]
, OH
Interest in the new field of aeronautics grew dramatically when the United States entered the World War I in 1917. The army chose Dayton as the site for a research-and-development program for military aviation because of the area’s transportation links to major cities and its engineering and testing facilities. McCook Field, north of downtown between Keowee Street and the Great Miami River, was charged with researching, developing, and testing military airplanes and accessories. For nearly a decade, many advancements in aviation occurred at McCook Field. They included new aircraft, controllable-pitch propellers, bulletproof gas tanks, free-fall parachutes, and night-observation cameras. In the 1920s, larger and more-powerful aircraft overwhelmed the small field, which featured a large sign to warn pilots: “This field is small. Use it all.” In 1927, aeronautical engineering was transferred to newly-created Wright Field, now a part of Wright-Patterson Air Force Base.
, OH
Zoar Separatists built the hotel in 1833 to accommodate overflow travelers from their original Ohio & Erie Canal inn. The hotel proved an economic boon to the Zoar community, but, by bringing the outside world into Zoar, ultimately became a source of discontent for members. During its heyday, the Zoar Hotel catered to curiosity-seekers, visiting artists, and families escaping the summer heat of nearby cities. Notable guests included Marcus Hanna and President William McKinley. The original structure was enlarged several times, including the now demolished 1892 Queen Anne addition which doubled the accommodations. By the mid-twentieth century, the hotel remained open as a popular restaurant with Rathskeller bar until closing to the public in July 1983. The exterior was restored by the Ohio History Connection in 2001-2002.