, OH
Stars of the silent screen, Lillian and Dorothy Gish enjoyed long and distinguished careers both in film and on stage. They began their careers as child actresses, performing in touring theater companies. Although Lillian was born in Springfield, Ohio, and Dorothy in Dayton, the Gish sisters considered Massillon their home, often staying here with relatives between plays and films. In 1912, Lillian and Dorothy went to New York and made their first film, An Unseen Enemy, with famed director D.W. Griffith.
, OH
The first African American congregation and first African American Methodist Episcopal (AME) Church in Dayton trace their roots back to the early 1830s. They were organized by Father Thomas Willis and a small group of faithful men and women. After several moves, the congregation settled on Eaker Street and the church was dedicated in the early 1870s. The church was rededicated in 1882 and renamed Wayman Chapel AME Church. The eminent poet Paul Laurence Dunbar and his mother Matilda attended and worshiped at the Eaker Street church. His untimely death in 1906 brought family and friends to his funeral services held at the church. By 1923 church leadership felt the need for more secure space for the growing congregation and moved to a new building at Fifth and Banks streets. Three elegant chandeliers for the sanctuary were donated by the city’s newspaper, the Dayton Daily News. (Continued on other side)
, OH
The Hotel Ashtabula was built in 1920 during an economic boom that lasted most of that decade. Architecturally, it represents a combination of Second Renaissance Revival and Georgian Revival styles. The H.L. Stevens and Company of Chicago and New York designed and built the hotel and others like it in Cleveland, Dayton, and Warren, Ohio and throughout the Midwest. The building included a ball room accommodating 300, a dining room that could seat 125, and club meeting and social rooms. A prominent structure of this downtown street, the Hotel Ashtabula was a hub for social activity. (Continued other side)
, OH
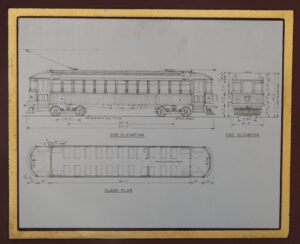
The Dayton, Springfield, and Urbana Electric Railway (DS&U) was an “Interurban” rail system that ran between the cities of Urbana, Springfield and Dayton. Its beginning can be traced to the franchise given to William H. Hanford to operate a single line of electrical railway between Springfield and the southern boundary of Champaign County in 1895. Hanford then sold his rights to John G. Webb of Springfield and Colonel Frederich Colburn of Kentucky, who along with other syndicate members formed the Dayton, Springfield, and Urbana Electric Railway. In 1897 Boston promoter Arthur E. Appleyard joined the syndicate and brought investment monies, organizational skills, and energy to the venture. He quickly became managing director/treasurer and the real driving force of the DS&U. The railway was organized into two divisions. One operated between Dayton and Springfield and the other between Springfield and Urbana. [continued on other side]
, OH
Reverend Lorenzo Langstroth, renowned as “The Father of American Beekeeping,” lived in this simple two-story, eight-room house with his wife, Anne, and their three children from 1858 to 1887. Unchanged externally, the Greek Revival cottage features brick pilasters and pediments and a fan-shaped front window. In his garden workshop, Langstroth made experimental beehives, established an apiary, and on the ten acres that surrounded his home, grew buckwheat, clover, an apple orchard, and a “honey garden” of flowers. He imported Italian queen bees in efforts to improve native bees and shipped his queens to keepers across the United States and around the world. The Langstroth Cottage was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976 and designated a National Historic Landmark in 1982. (Continued from other side)
, OH
Natalie Clifford Barney was born in Dayton on October 31, 1876. Her family was wealthy and industrious, including her great grandfather who founded the Dayton Academy, Cooper Female Seminary, and Dayton Car Works. Natalie, who knew that she was a lesbian by age twelve, lived an outspoken and independent life unusual for a woman of this time period. Her openness and pride about her sexuality, without shame, was at least one hundred years ahead of its time. She published Some Portrait-Sonnets of Women, a book of love poems to women under her own name in 1900. American painter Romaine Brooks was Barney’s partner and companion for fifty years. (continued on other side)
, OH
Trenton’s founder, Michael Pearce, came to the area in 1801. The original village of 33 lots was named Bloomfield. When the post office was established in 1820, it was named Trenton to honor the founder’s home state of New Jersey. Pearce’s son-in-law, Squier Littell, was the first resident doctor in Butler County. Originally settled by the English, Trenton saw a migration of Germans by 1840. By 1851, the farming community became a grain center with the introduction of the Cincinnati, Hamilton, and Dayton Railroad. Further development occurred when a franchise was granted to operate interurban electric traction cars through the village in 1896. Early commercial endeavors were Dietz, Good & Company grain elevator, Trenton Foundry, and Magnode Corporation. By 1991, the largest industries were Miller Brewing Company and Cinergy/Cincinnati Gas & Electric.
, OH
Born in Alexandria in 1853, Willoughby Dayton Miller received his primary education in a nearby one-room schoolhouse. He graduated from the University of Michigan in 1875 and then studied in Edinburgh, Scotland. Later, he traveled to Berlin, Germany where he met an expatriate American dentist, Dr. Frank Abbot, who encouraged him to study dentistry. Graduating from the University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine in 1879, Miller returned to Berlin and joined Abbot’s practice. Two years later, he gained a research appointment at the University of Berlin where he embarked on a career that brought the science of bacteriology into dentistry. In 1889, he published his research findings of the study of oral bacteria and the process of dental caries (tooth decay) entitled The Micro-Organisms of the Human Mouth. For his work, Miller is credited as the first to accurately describe the process of tooth decay. (Continued on other side)